深度优先遍历
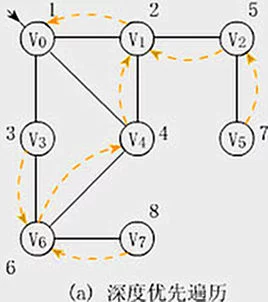
深度优先搜索,是图论中的经典算法。其利用深度优先搜索算法可以产生目标图的相应拓扑排序表,利用拓扑排序表可以方便的解决很多相关的图论问题,如最大路径问题等等。
- 中文名 深度优先遍历
- 外文名 Depth-First Traversa
- 学科 数据结构
- 属于 图
递归定义
深度优先遍历(Depth-First Traversal)
假设给定图G的初态是所有顶点均未曾访问过。在G中任选一顶点v为初始出发点(源点),则深度优先遍历可定义如下:首先访问出发点v,并将其标记为已访问过;然后依次从v出发搜索v的每个邻接点w。若w未曾访问过,则以w为新的出发点继续进行深度优先遍历,直至图中所有和源点v有路径相通的顶点(亦称为从源点可达的顶点)均已被访问为止。若此时图中仍有未访问的顶点,则另选一个尚未访问的顶点作为新的源点重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点均已被访问为止。
图的深度优先遍历类似于树的前序遍历。采用的搜索方法的特点是尽可能先对纵深方向进行搜索。这种搜索方法称为深度优先搜索(Depth-First Search)。相应地,用此方法遍历图就很自然地称之为图的深度优先遍历。
过程
设x是当前被访问顶点,在对x做过访问标记后,选择一条从x出发的未检测过的边(x,y)。若发现顶点y已访问过,则重新选择另一条从x出发的未检测过的边,否则沿边(x,y)到达未曾访问过的y,对y访问并将其标记为已访问过;然后从y开始搜索,直到搜索完从y出发的所有路径,即访问完所有从y出发可达的顶点之后,才回溯到顶点x,并且再选择一条从x出发的未检测过的边。上述过程直至从x出发的所有边都已检测过为止。此时,若x不是源点,则回溯到在x之前被访问过的顶点;否则图中所有和源点有路径相通的顶点(即从源点可达的所有顶点)都已被访问过,若图G是连通图,则遍历过程结束,否则继续选择一个尚未被访问的顶点作为新的顶点,继续遍历。
template <int max_size>void Digraph<max_size> :: depth_first(void (*visit)(Vertex &)) const
/* Post: The function *visit has been performed at each vertex of the Digraph in depth-first order.
Uses: Method traverse to produce the recursive depth-first order. */
{
bool visited [max_size];
Vertex v;
for (all v in G) visited [v] = false;
for (all v in G) if (!visited [v])
traverse (v, visited, visit);
}
template <int max_size>
void Digraph<max_size>::traverse(Vertex &v, bool visited[ ],void (*visit)(Vertex &)) const
/* Pre: v is a vertex of the Digraph.
Post: The depth-first traversal, using function *visit, has been completed for v and for all vertices that can be reached from v.
Uses: traverse recursively. */
{
Vertex w;
visited [v] = true;
(*visit) (v);
for (all w adjacent to v)
if (!visited [w])
traverse (w, visited, visit);
}
java代码如下:
//求DFS的深度优先递归算法
public class DNFSreach {
/**
* 这里是文档说明
* 算法如下
*开始
*Start;
*
* procedure DFS_visit(G,u)
* color[u] = Gray;//白色结点u已被发现
* for each edge (u,v)do
* if color[u] = White then
* DFS_visit(G,v);
* repeat color[u]=black;//完成后置u为黑色
* end;
*
* procedure DFS(G)
* for each vertex u 属于V do
* color[u] = white
* for vertex each u 属于 V do
* if color[u]=white
* then DFS_visit(G,u)
* repeat
*
*
* 构建一个无向图
* 无穷大表示这两个点无边,1表示两者有边
* 白色用1表示,灰色用2表示,黑色用3表示
* 初始状态均为白色
* 搜索中被发现的顶点置为灰色
* 结束时,即其邻接表被完全检索之后,其被置为黑色
* 构建一个color[8]数组,其中color[0]不用
* 初始化为0
* S表示无穷大
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
* -------------------------
* 0
* 1 s 1 1 s s s s s
* 2 1 s s 1 1 s s s
* 3 1 s s s s 1 1 s
* 4 s 1 s s s s s 1
* 5 s 1 s s s s s 1
* 6 s s 1 s s s 1 s
* 7 s s 1 s s 1 s s
* 8 s s s 1 1 s s s
*
* 深度优先搜索的结果应该为
* 1-2-4-8-5-3-6-7
*
* @param args
*/
static int color[];
static int d =0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int s = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int G[][]={{s,s,s,s,s,s,s,s,s},
{s,s,1,1,s,s,s,s,s},
{s,1,s,s,1,1,s,s,s},
{s,1,s,s,s,s,1,1,s},
{s,s,1,s,s,s,s,s,1},
{s,s,1,s,s,s,s,s,1},
{s,s,s,1,s,s,s,1,s},
{s,s,s,1,s,s,1,s,s},
{s,s,s,s,1,1,s,s,s}};
color = new int [9];
ProcedureDFS(G,9);
}
public static void ProcedureDFS(int [][]G,int n){
//图是以二维数组的形式保存
//n是二维数组的维数
for(int i=1;i <= n-1;i++){
color[i]=1;//把每一个顶点都置为白色,表示还没搜索
}
for(int i=1;i<= n-1;i++){
//对于每一个顶点没被访问的顶点进行访问
if(color[i] == 1){
DFS_visit(G,i);//遍历其访问的顶点
}
}
}
private static void DFS_visit(int[][] g, int i) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
color[i] = 2;//标志为灰色,表示被访问过
d++;
if(d != g.length-1)
System.out.print(""+i+" -> ");
if(d == g.length-1){
System.out.println(""+i);
}
for(int t=1;t<= g.length-1;t++){
//邻接点没有被访问到
if(color[t] == 1 && g[i][t] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
DFS_visit(g,t);
}
}
color[i] = 3;//标志位黑色
}
}
最小花费举例:
package test1;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Deptfsearch {
static int Answer, N, sum, cost;
static int[][] input, mark;
static int[] visit;
static boolean check() {
for (int v = 1; v <= N; v++) {
if (visit[v] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static void Try(int u) {
if (check()) {
if (input[u][1] != 0 && Answer > cost + input[u][1])
Answer = cost + input[u][1];
return;
}
if (Answer < cost)
return;
for (int v = 1; v <= N; v++) {
if (input[u][v] != 0 && visit[v] == 0) {
visit[v] = 1;
cost = cost + input[u][v];
Try(v);
cost = cost - input[u][v];
visit[v] = 0;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
sc = new Scanner(new FileInputStream("sample_input.txt"));
int T = sc.nextInt();
for (int test_case = 0; test_case < T; test_case++) {
sum = 0;
cost = 0;
N = sc.nextInt();
input = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
mark = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
visit = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
input[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
sum = sum + input[i][j];
}
}
Answer = sum + 1;
visit[1] = 1;
if (N == 1)
Answer = input[1][1];
else
Try(1);
// Print the answer to standard output(screen).
System.out.println("Case #" + (test_case + 1));
System.out.println(Answer);
}
}
}